Male infertility affects millions of individuals worldwide. It’s a complex condition described as a man’s inability to make their fertile female partner pregnant after unprotected sexual intercourse for a significant period, typically one year. While the causes of infertility in men can vary, urological conditions are among the leading contributors.
Urological conditions are medical issues or disorders that affect the organs and structures within the urinary system and male reproductive system. These conditions can impact various parts of the male reproductive organs, such as the testes, epididymis, prostate gland, and penis.
If you have infertility concerns, it’s best to consult an expert on the matter. In Queenstown & Wanaka, Auckland, or Dunedin, you can get in touch with Dr. Amir Zarrabi, a urology and male infertility specialist. Dr. Zarrabi can help you determine whether you are experiencing any one of these urological conditions that are commonly linked to male infertility:

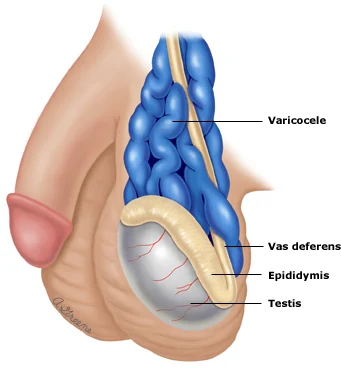
Varicocele
Varicocele is one prevalent cause of male infertility. It’s a condition characterised by the enlargement of veins within the scrotum. It’s been found to affect approximately 15% of men and 40% of infertile men. The reason varicocele has been linked to infertility is that it can make the blood flow from the testicular veins abnormal. It can also impair scrotal thermoregulation, which can increase testicular temperature. Both can lead to impaired sperm production and quality.
Fortunately, varicocele can be treated. It typically involves surgical repair, known as varicocelectomy. During this procedure, the dilated veins are ligated or removed to improve blood flow and reduce scrotal temperature. In cases where surgery is not feasible or effective, assisted reproductive techniques, like in vitro fertilisation, may be recommended to achieve pregnancy.
Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) has also been linked to male fertility. It’s characterised by a man’s inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse, which is crucial for successful intercourse and conception. ED may arise from various factors, including vascular issues, hormonal imbalances, or neurological disorders. It can also be due to psychological factors such as stress or anxiety.
The good news about this condition is that there are treatment options available. Individuals with erectile dysfunction can take oral medications, like phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors, or opt for more invasive interventions, like penile implants. Once ED is addressed, it improves sexual function and enhances fertility outcomes.
Hypospadias
Hypospadias is a congenital condition where the urethral opening is located on the underside of the penis rather than at the tip. This abnormal positioning can prevent normal urine flow and interfere with semen deposition during intercourse, which potentially impacts a man’s fertility.
Surgical correction of hypospadias is typically recommended to restore normal urinary and reproductive function. The procedure aims to reposition the urethral opening at the tip of the penis. This improves urinary flow and enhances fertility outcomes. Surgical outcomes are generally favourable, and individuals with corrected hypospadias can often achieve normal fertility.
Undescended Testicles
Another urological condition that can affect male fertility is undescended testicles or cryptorchidism. It’s when one or both testicles fail to descend into the scrotum before birth. Men with this condition are more at risk of infertility later in life due to impaired sperm production and function.
Treatment for undescended testicles includes hormonal therapy to stimulate testicular descent. The condition can also be treated through surgical correction, known as orchidopexy. This is when the testicle(s) are repositioned into the scrotum. Keep in mind that undescended testicles must be addressed early to prevent long-term fertility complications and ensure optimal reproductive health.
Urological Infections
At times, urological infections can adversely affect male fertility. Epididymitis, prostatitis, and urinary tract infections can lead to inflammation in the reproductive organs. This disrupts sperm production and motility and impairs overall sperm quality.
Typically, urological infections are diagnosed through a thorough medical history review, a physical examination, and laboratory tests such as urine culture and semen analysis. When it comes to treating such infections, the doctor may advise antibiotics and antimicrobial therapy to eradicate the infection. They might also suggest lifestyle modifications and prevention strategies to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Ejaculatory Duct Obstruction
Ejaculatory duct obstruction occurs when the ducts that transport semen from the seminal vesicles to the urethra become blocked or obstructed. This obstruction can prevent the ejaculation of semen during orgasm, which can lead to infertility or reduced fertility.
When it comes to managing ejaculatory duct obstruction, the underlying cause of the blockage must be addressed, and the normal flow of seminal fluid needs to be restored. In the case of transurethral resection of ejaculatory ducts, it creates a clear passage for seminal fluid to pass through the ejaculatory ducts during ejaculation.
It’s a surgical procedure that involves the removal or dilation of the obstructed portion of the ejaculatory duct. If the obstruction is caused by narrowing or strictures in the ejaculatory ducts, balloon dilation or stent placement is a treatment option. It widens the ducts and improves semen flow.
Urological conditions can also significantly impact male fertility. However, with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, many individuals can overcome their infertility challenges. If you’re experiencing fertility concerns, seek medical evaluation and guidance from a qualified healthcare provider. In particular, consult a urology and male infertility specialist. With the right support and treatment, you can manage urological conditions and make parenthood possible.