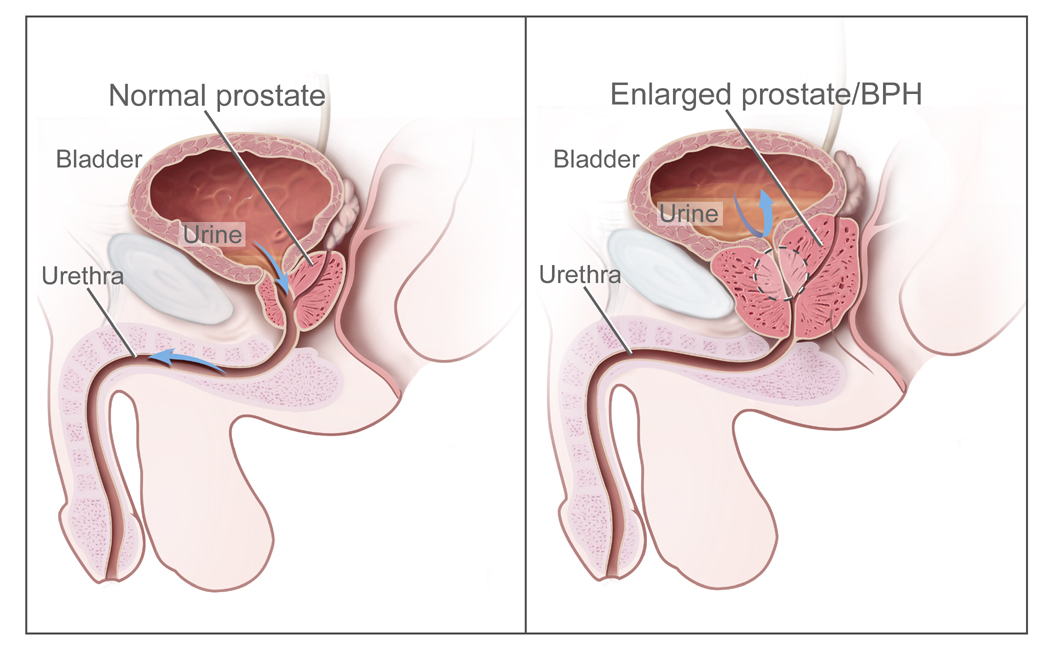
The prostate gland lies underneath the bladder and surrounds the urethra.
Enlargement of the prostate is a natural process as men get older. An enlarged prostate only becomes a concern when it leads to problems with urination. The exact cause of prostate enlargement is unknown: male hormones (testosterone) are needed for this process and may play a role and there may also be a familial tendency.
An enlarged prostate does not put you at a higher risk of developing prostate cancer.
What are the symptoms of prostate enlargement? (BPH)
A person with prostate enlargement may suffer from the following symptoms:
- Slow flow and prolonged urination. Sometimes you feel that you need to push to be able to get the urine out.
- Inability to start urinating immediately when you go to the toilet (hesitancy). You have to wait before urine starts to flow.
- Dribbling of urine towards the end of urination. Sometimes this results in wet and smelly underwear.
- A feeling of incomplete emptying of your bladder.
- Frequent desire to pass urine. It may be associated with the need to wake up several times at night to urinate.
- Urgency – when you feel that your bladder is full and you need to urinate, you have to get to the toilet very quickly and cannot postpone urination.
- Prolonged and severe blockage to urine flow from the bladder may in later stages lead to damage to the bladder and kidneys (kidney failure).
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder can result in recurrent bladder infections and even bladder stones.
As a Urologist, I feel passionate about the importance of having prostate enlargement (BPH) properly assessed.
If left untreated, an enlarged prostate can lead to potentially serious problems like:
- Acute retention of urine. This is the total inability to pass any urine resulting in an over-filled and very painful bladder. It will require urgent bladder drainage by placement of a urinary catheter.
- Recurrent bladder infections.
- Bladder stones.
- Blood in the urine, sometimes with clots.
- Kidney damage / kidney failure.
In my practice, I see men with enlarged prostates (BPH) and urinary symptoms every week.
During the consultation, I will assess the effects and severity of prostate enlargement as this will determine our treatment strategies. The following tests may be done at the time of your consultation:
- International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS): You may be asked to complete a form that contains a set of questions designed to assess the severity of your urination symptoms.
- Urine test to check for infection.
- Finger examination of your prostate (also called digital rectal examination / DRE).
- Blood tests to check your kidney function.
- PSA blood test to assess your risk of prostate cancer.
- Urine flow test to measure the strength of urine flow.
- An ultrasound scan to check for adequate bladder emptying.